ECG
An Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a simple, non-invasive test used to assess the heart's rhythm and electrical activity. Small sensors attached to the skin detect the electrical signals generated by the heart with each beat. These signals are recorded and analyzed by a doctor to identify any abnormalities.
2D ECHO
2D Echo with Doppler is a non-invasive ultrasound examination used to assess heart health. It helps detect cardiac abnormalities, evaluate heart function and ejection fraction, assess valve motion, and identify fluid around the heart. This test is also commonly used as a pre-operative fitness evaluation.
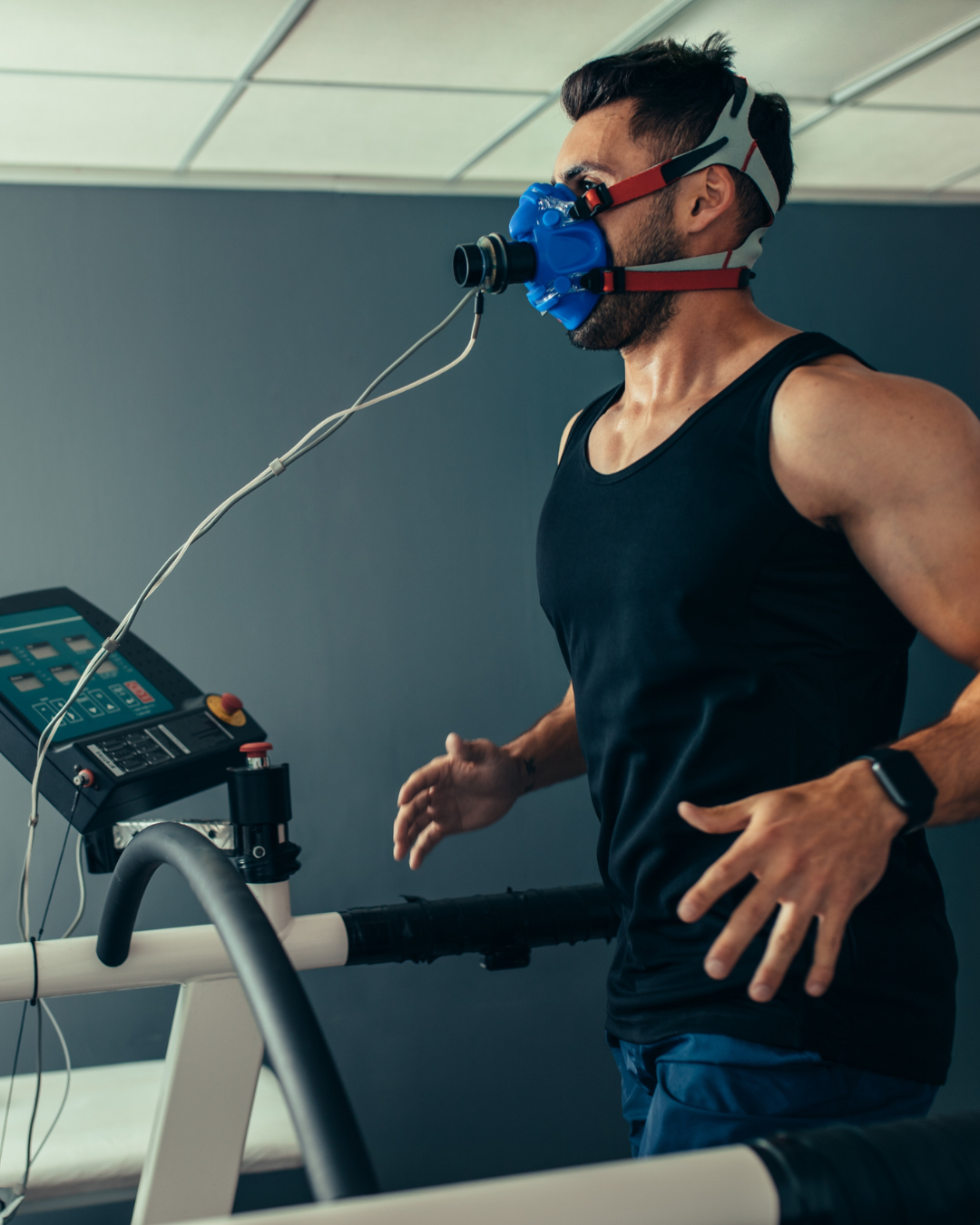

Treadmill Test (TMT)
A Treadmill Test (TMT), also known as a stress test, is a diagnostic procedure that monitors heart function during exercise. It helps compare blood circulation in the heart at rest and under physical stress, making it an essential test for detecting coronary artery diseases and abnormal heart rhythms.
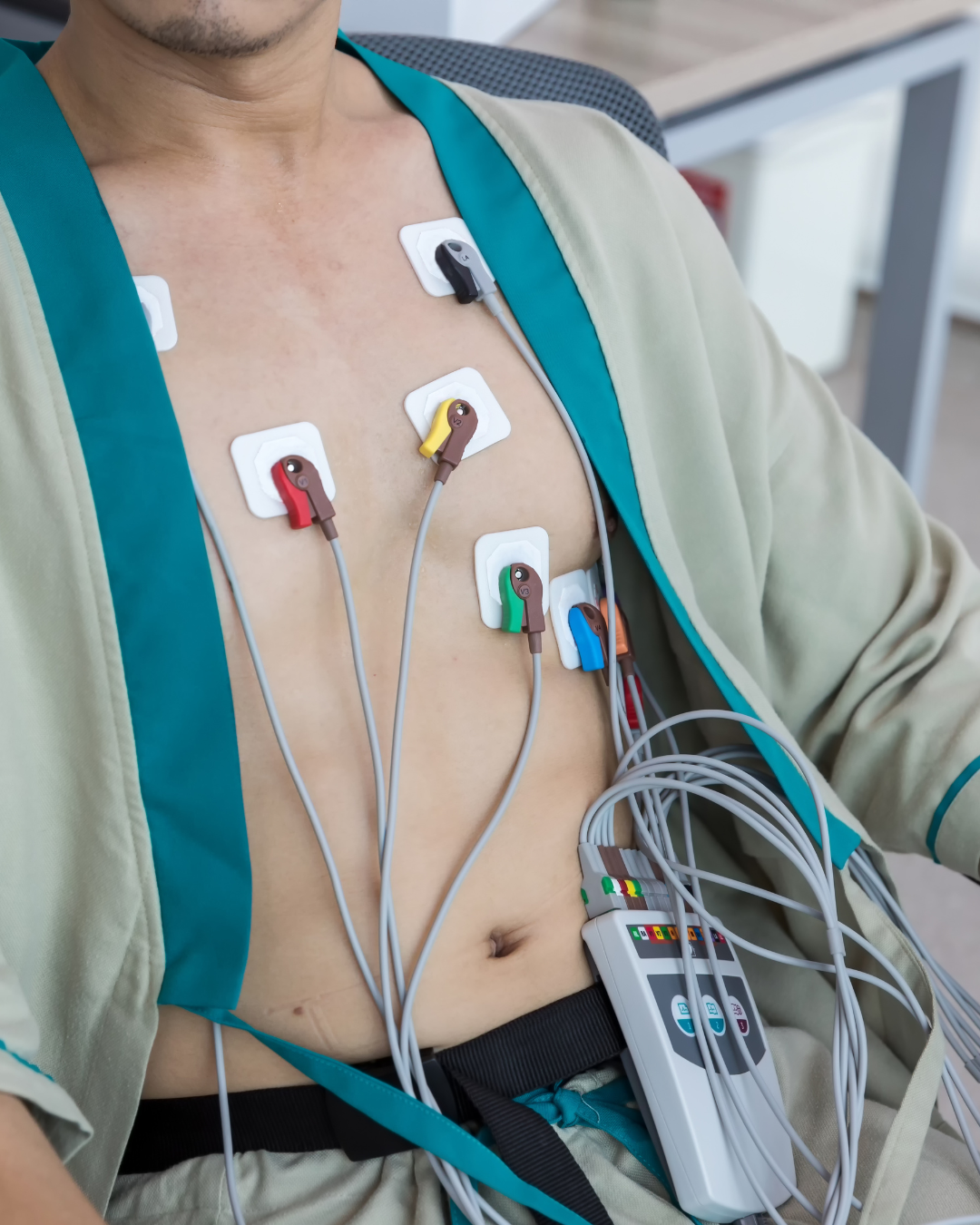
Holter Monitor
A Holter monitor is a small, portable device that continuously records the heart's rhythm and electrical activity over an extended period. It is used to detect irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) that may not appear during a standard Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG).
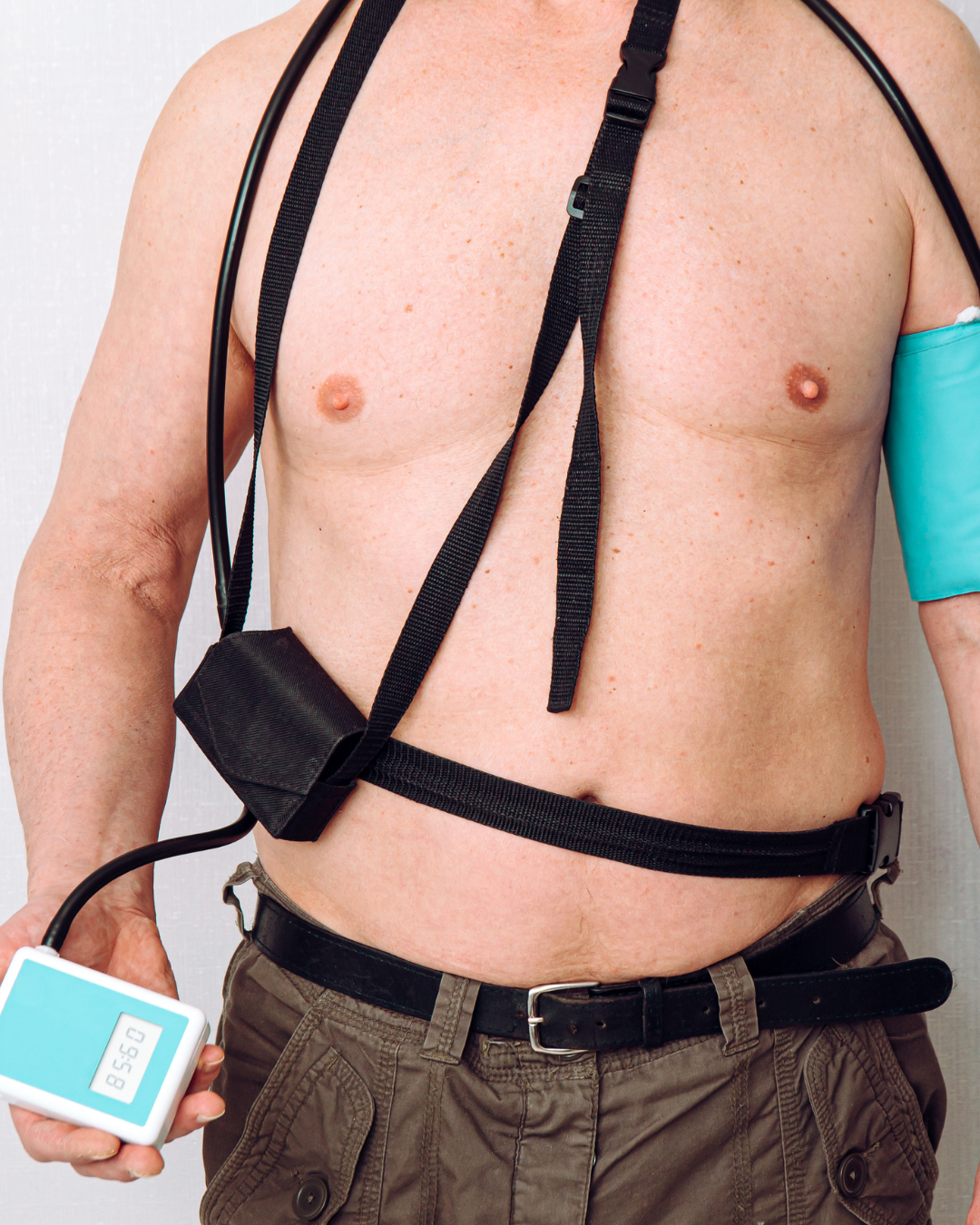
24 ABPM Test
A 24-hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM) test measures your blood pressure at regular intervals over 24 hours while you go about your normal daily activities, helping to diagnose and monitor high blood pressure or hypertension.

PAMI/PPCI
Primary Angioplasty in Myocardial Infarction (PAMI) or Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PPCI) is a life-saving emergency procedure performed in patients experiencing an ongoing myocardial infarction (heart attack).
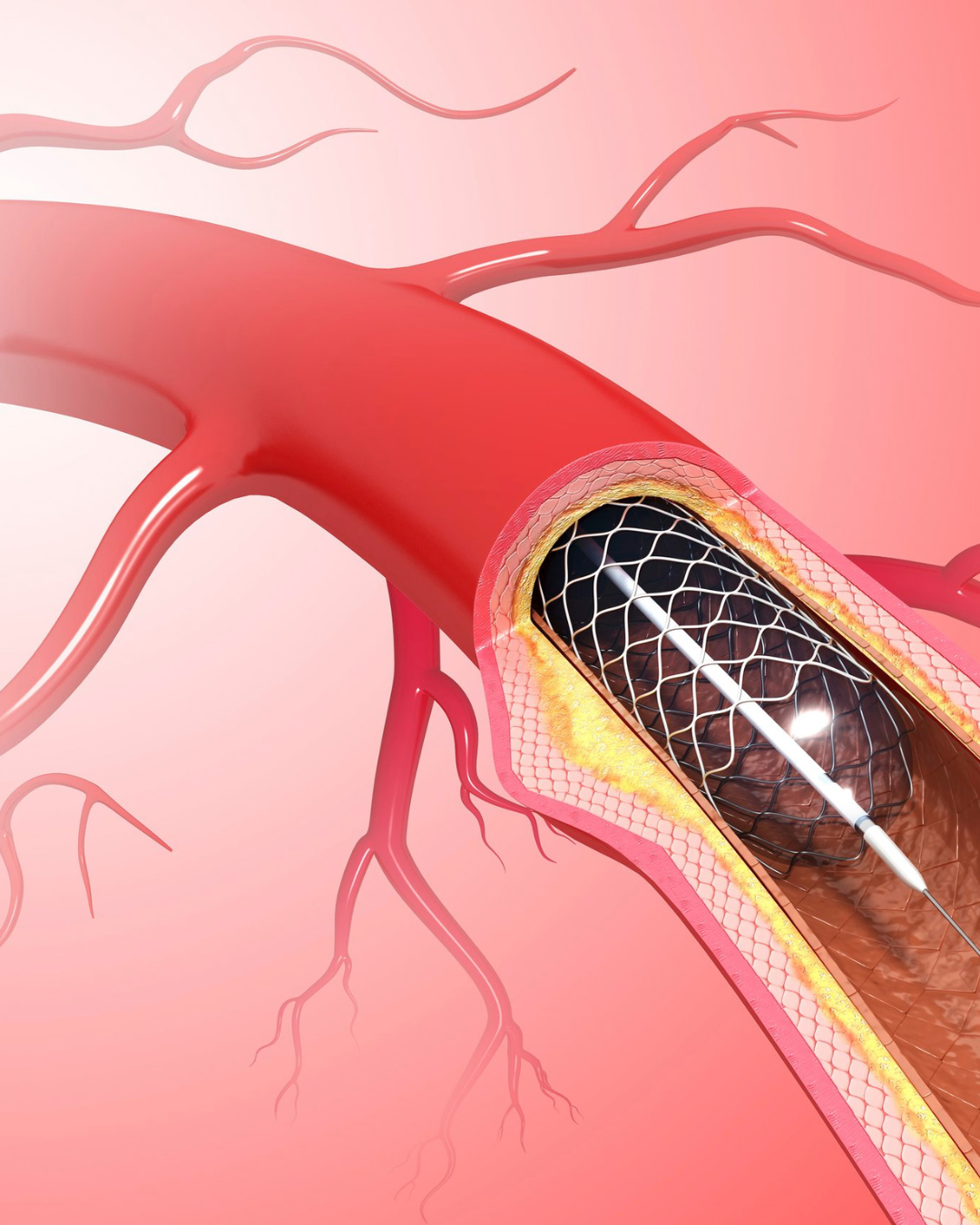
Coronary Angioplasty
Coronary angioplasty, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a minimally invasive procedure used to open clogged heart arteries and restore blood flow to the heart.
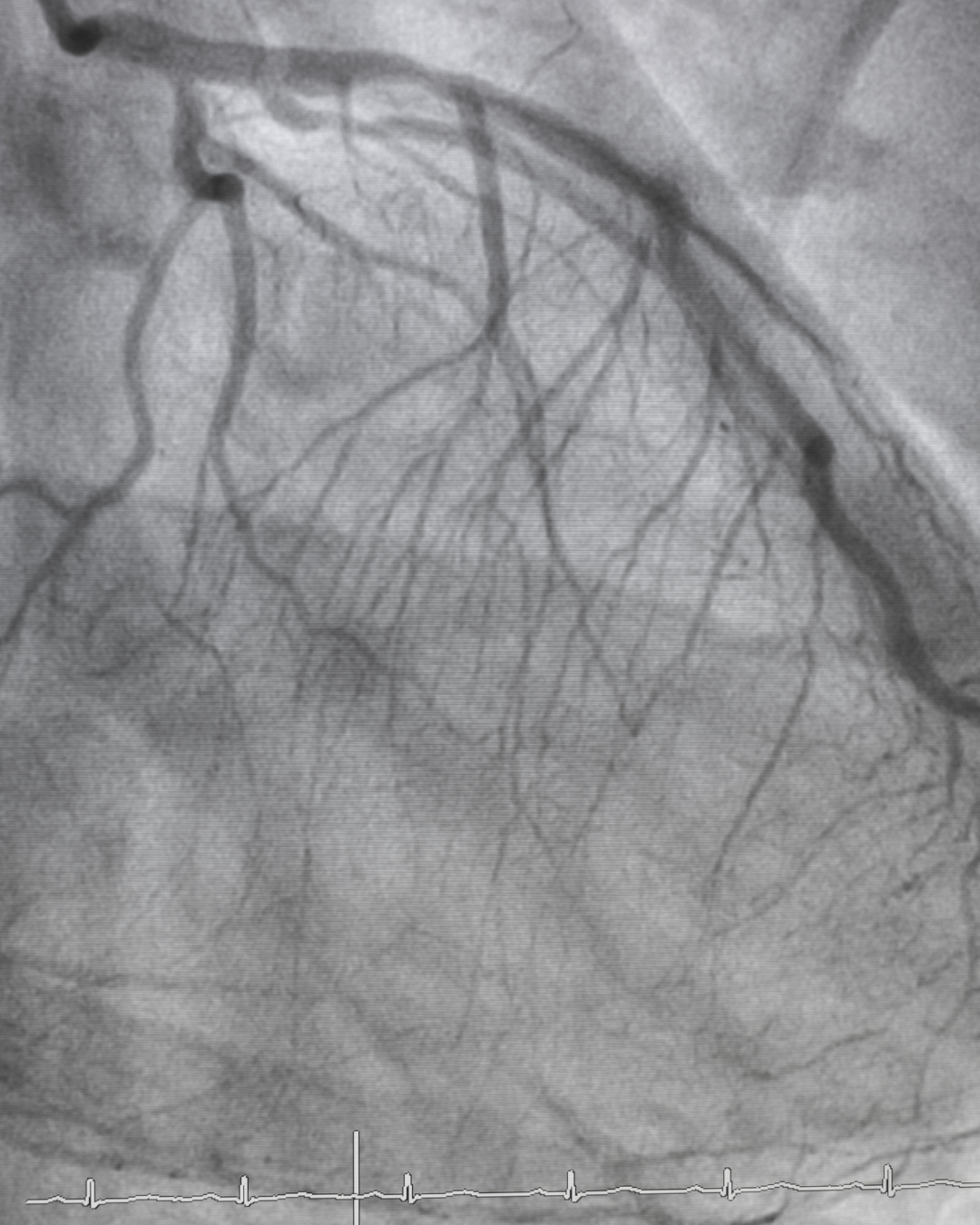
Coronary Angiography
Coronary angiography is a diagnostic procedure that uses a special dye (contrast material) and X-rays to visualize blood flow through the arteries of the heart. It helps detect blockages and assess heart health.
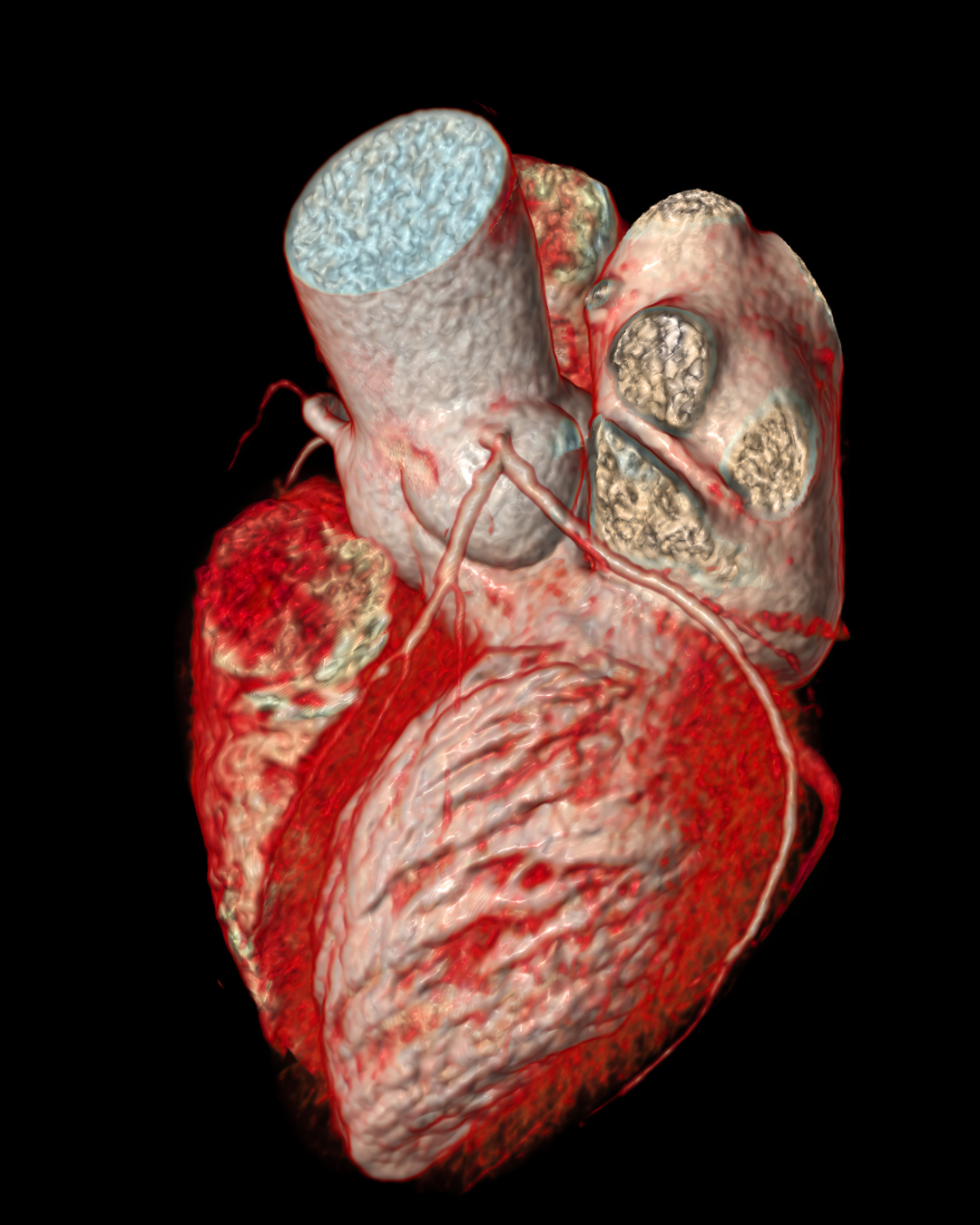
Coronary Imaging
A Computerized Tomography (CT) Coronary Angiogram is a non-invasive imaging test used to examine the arteries supplying blood to the heart. This test utilizes a high-resolution X-ray machine to generate detailed images of the heart and its blood vessels. It helps diagnose various heart conditions, detect narrowed or blocked arteries, and guide further treatment plans.
Coronary Physiology
Coronary physiology refers to the study of how blood flows through the coronary arteries, which supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle (myocardium). It plays a critical role in diagnosing and managing coronary artery disease (CAD) and assessing the functional significance of arterial blockages.
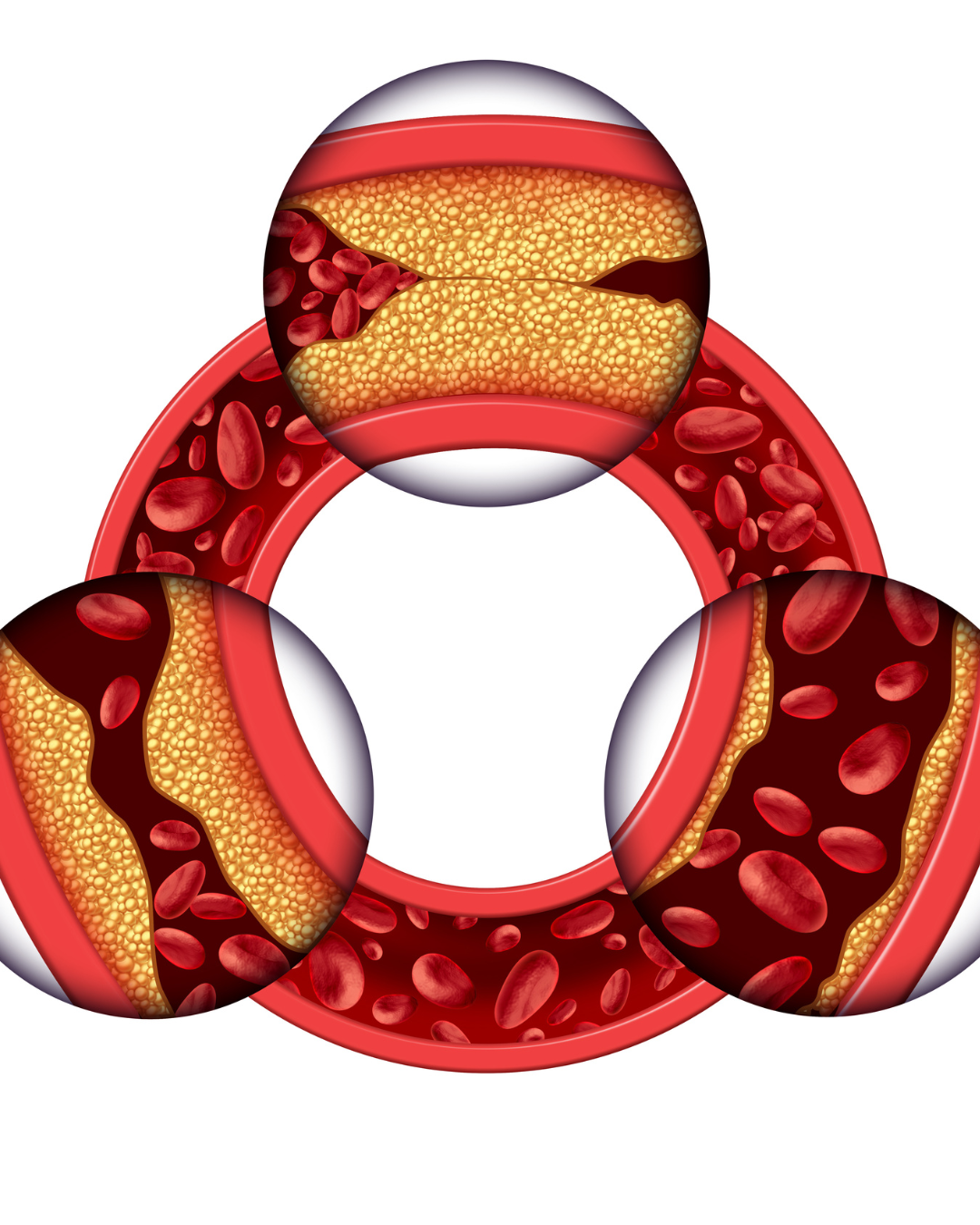
Coronary Rotablation
Coronary Rotablation, also known as Rotational Atherectomy, is a specialized procedure used to break down heavily calcified plaques in the coronary arteries. This technique is employed when traditional balloon angioplasty fails to effectively open a blocked artery due to severe calcification.
Coronary Laser
Coronary Laser Angioplasty is a specialized technique used to remove blockages in the coronary arteries using laser energy. This method is particularly useful in cases where standard balloon angioplasty and stenting may not be effective, such as in heavily calcified or complex lesions.
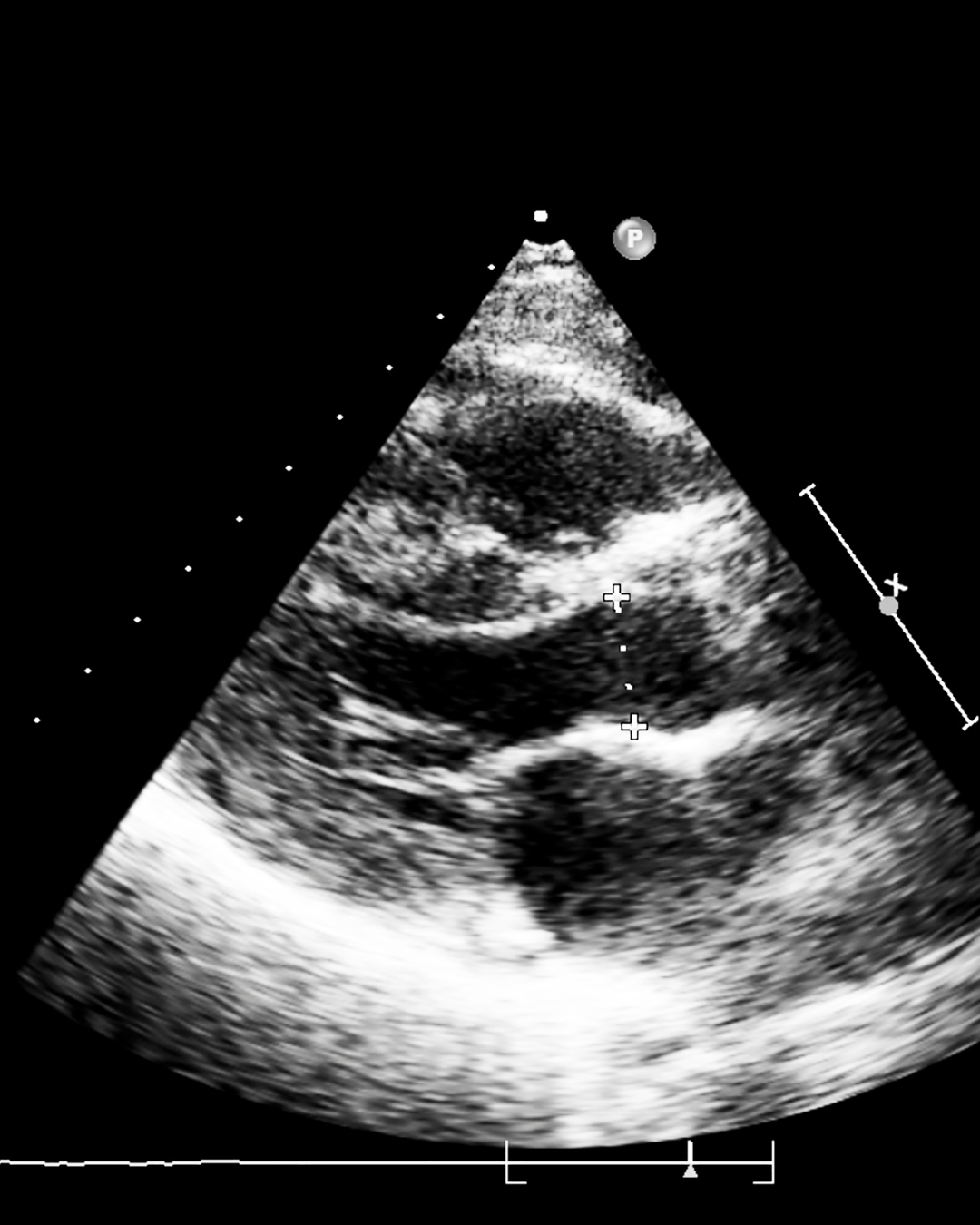
TEE
A transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) is an advanced imaging test that uses sound waves to create highly detailed images of the heart. Unlike standard echocardiograms, which capture images from outside the chest, TEE provides a clearer view from inside the body. During the procedure, a healthcare provider guides a thin, flexible tube down the esophagus, allowing for precise visualization of the heart’s structure and function. This test is particularly useful for detecting blood clots, infections, and other cardiac conditions.

TAVI/TAVR
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) or Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) is an advanced minimally invasive procedure that replaces a diseased aortic valve without removing the old, damaged valve. Instead, the new valve is implanted within the existing valve, restoring proper heart function.
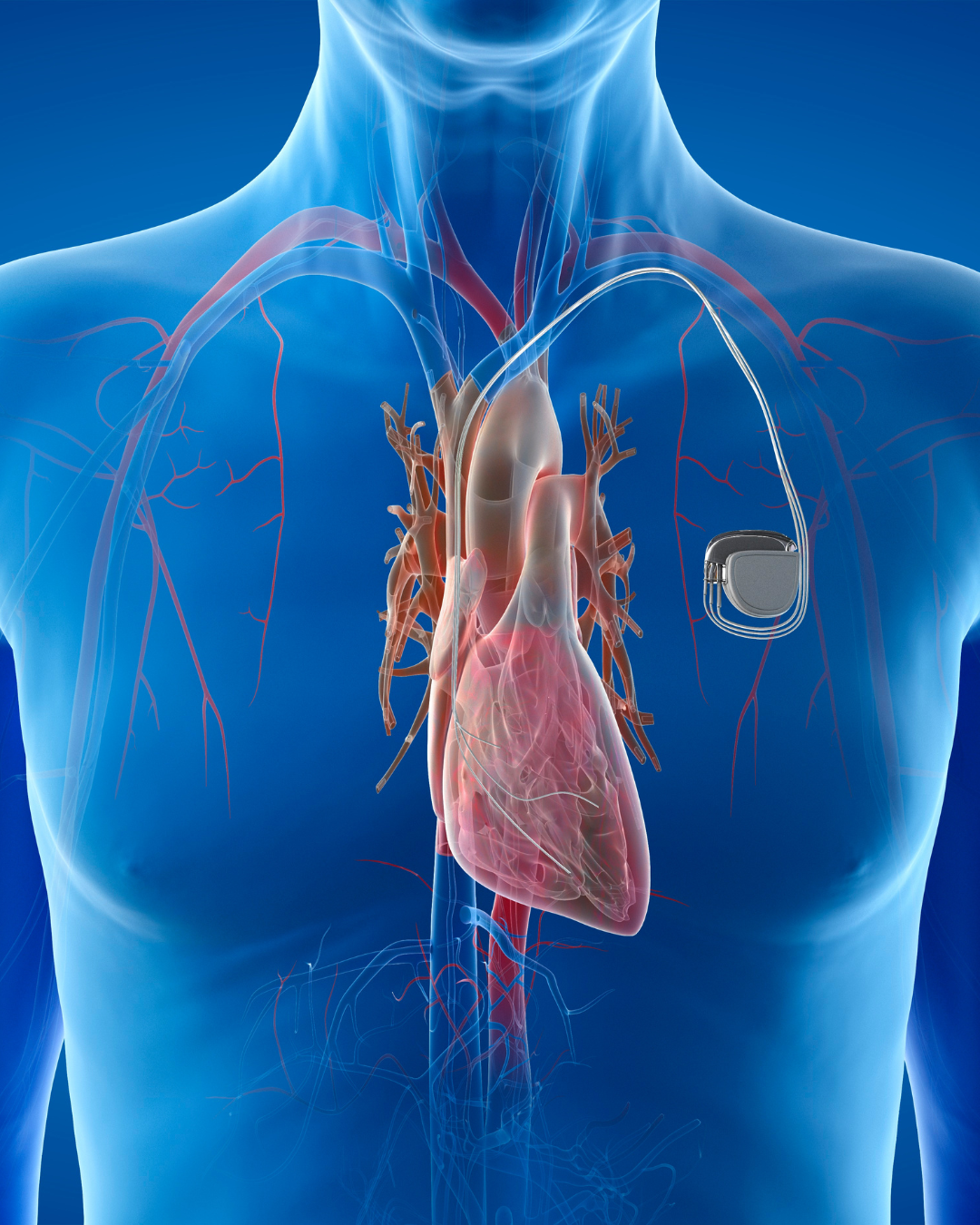
Pacemaker Implantation
A pacemaker is a small, battery-operated device that helps regulate an irregular heartbeat. It is implanted under the skin, typically near the collarbone, and connected to the heart with thin wires. The device sends electrical impulses to stimulate the heart when it beats too slowly (bradycardia) or irregularly.
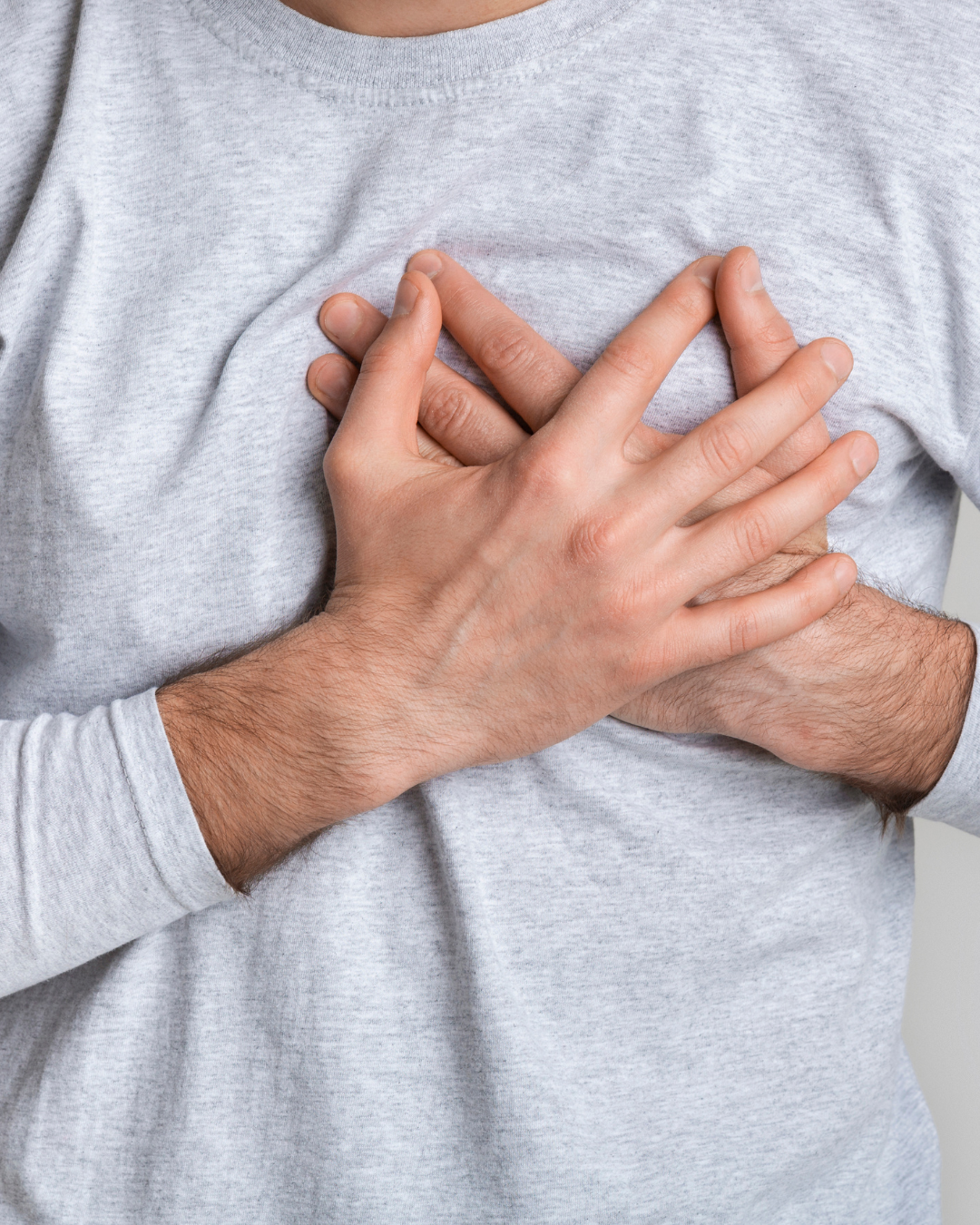

Heart Attack Treatment
A heart attack (myocardial infarction) occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, usually due to a blood clot in a coronary artery. Prompt treatment is crucial to restore blood flow and minimize heart damage.
